Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries have gained popularity in recent years due to their superior performance and safety compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. They are widely used in electric vehicles, portable electronics, and renewable energy storage systems. While LiFePO4 batteries offer numerous advantages, proper charging practices are crucial to maximize their efficiency, lifespan, and safety.
In this article, we are here to explore that how to charge your LiFePO4 battery with different voltage, learn about charging in parallel and series, and choose the best LiFePO4 battery charger.
Table of Content
- 1. Understanding LiFePO4 Batteries
- 2. Three Methods of Charging LiFePO4 Batter
- 2.1 Constant Current Charging
- 2.2 Constant Voltage Charging
- 2.3 Constant Current & Constant Voltage (CC/CV)
- 3. Charging LiFePO4 Batteries in Parallel
- 4. Charging LiFePO4 Batteries in Series
- 5. Safe Charging Guidelines for LiFePO4 Batteries
- 6. Safety Instruction During Charging LiFePO4 Battery
- 7. How to Charge LiFePO4 Batteries with Solar?
- 8. FAQs on Charging LiFePO4 Battery
Understanding LiFePO4 Batteries
LiFePO4 batteries are a type of lithium-ion battery known for their stability and safety features. Unlike other lithium-ion chemistries, LiFePO4 batteries are less prone to thermal runaway, which significantly reduces the risk of fire or explosion, especially during charging.
Key characteristics of LiFePO4 batteries include:
Safety: They are inherently safer due to the stable chemical structure and high thermal stability.
Longevity: LiFePO4 batteries typically have a longer lifespan compared to other lithium-ion batteries, with a high number of charge-discharge cycles.
Performance: They offer high power density, making them suitable for applications requiring quick discharge rates.
Three Methods of Charging LiFePO4 Batter
After long-term usage of LiFePO4 Batteries, the battery power will need to be replenished in time. Here are the most common methods to charge a LiFePO4 battery.
1. Constant Current Charging
It means keeping the charging current constant throughout the charging process. This charging method is simple to operate and implement, and the charging power is also easy to calculate.
However, during the charging time increases, the battery's ability to receive current will decrease in the later stage of charging, and the corresponding charging current utilization rate will also be greatly reduced.
2. Constant Voltage Charging
The constant voltage charging is to keep the voltage constant during the charging process. The charging current will automatically adjust. If the voltage constant value specified is appropriate, then not only can the battery be fully charged, but also gassing and water loss can be reduced.
The disadvantaged of this charging method is that it cannot effectively reflect the overall charging status of the battery. Additionally, if the current is too large, the charger will cause damage to the power battery.
3. Constant Current & Constant Voltage (CC/CV)
This is the most recommend charging method for LiFePO4 batteries. Initially, the charger supplies a constant current until the battery voltage reaches a set threshold, after which it switches to constant voltage mode until the current drops to a low level.
In short, it is a combination of constant voltage charging and constant current charging. Redodo LiFePO4 battery charger uses this charging method. The charging mode not only avoids overcharging, but also avoids excessive charging current, which can play a good role in protecting the battery.
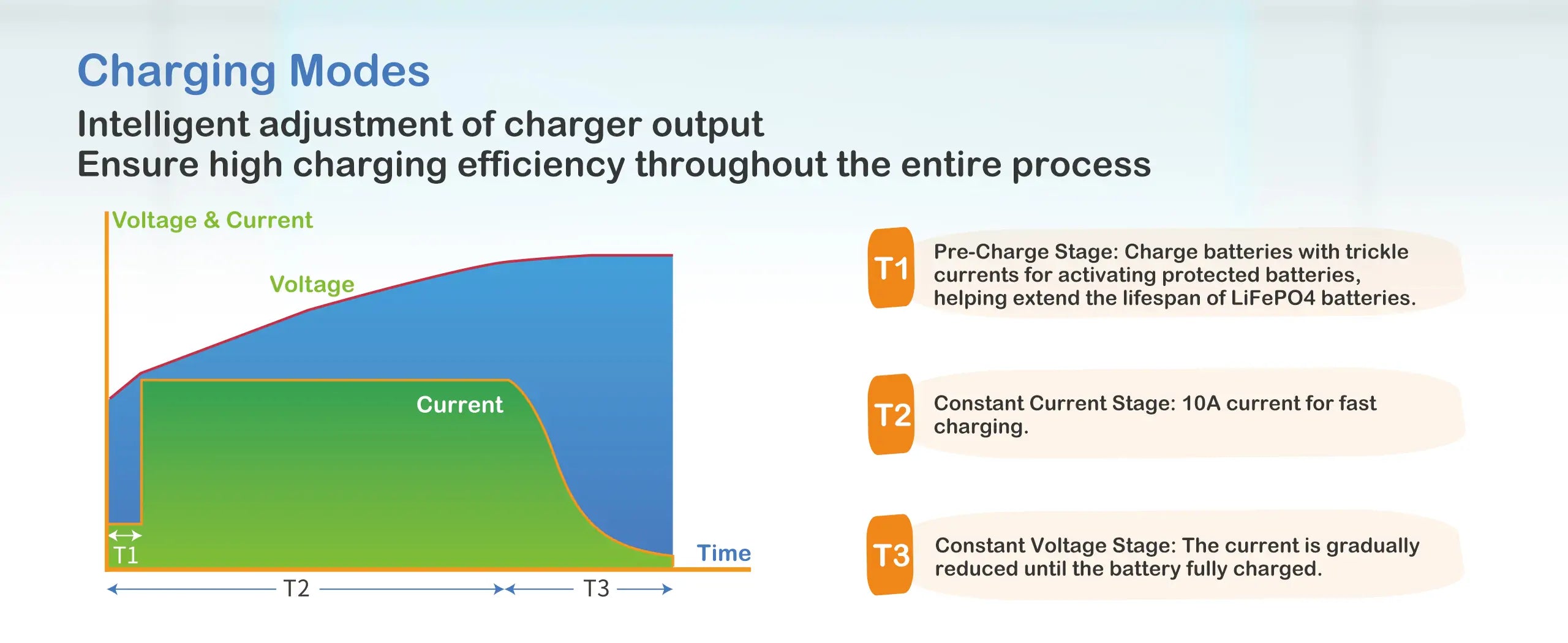
The method involves three main stages:
Pre-Charge Stage: The charger provides trickle charging with a small and continuous current. It helps protect the LiFepo4 batteries and extend their lifespan.
Constant Current (CC) Stage: During this stage, the charger supplies a constant current to the battery. The current level is typically set based on the battery's capacity, often ranging from 0.2C to 0.5C (where C is the battery's capacity in ampere-hours).
Constant Voltage (CV) Stage: Once the battery voltage reaches a predefined level (typically around 3.6V per cell), the charger switches to constant voltage mode. In this stage, the charger maintains a constant voltage while allowing the charging current to decrease gradually as the battery approaches full charge.
Charging LiFePO4 Batteries in Parallel
When connecting LiFePO4 batteries in parallel, you need to ensure each battery is within 0.1V of each other before placing them in service. This practice minimizes the risk of imbalance between batteries, which can affect overall performance and longevity. Here are the recommended charging voltage parameters based on system voltage:

These voltage ranges apply to both constant current (CC) and constant current-constant voltage (CC-CV) charging profiles. If your charger operates below these specified voltages, the battery may be undercharged, leading to reduced capacity. Chargers exceeding these voltage ranges may trigger the battery management system (BMS) to disconnect the battery, necessitating the removal of the load to reconnect.
To avoid these issues, it is advisable to invest in a high-quality LiFePO4 battery charger, for example, Redodo 12V LiFePO4 Battery Charger, that meets these voltage requirements.

Charging LiFePO4 Batteries in Series
When connecting LiFePO4 batteries in series, each battery should ideally be within 50mV (0.05V) of each other before integrating them into service. This precaution helps minimize the potential for imbalance between batteries, which can adversely affect performance and longevity.
For charging LiFePO4 batteries in series, consider using a multi-bank charger that can charge each battery individually. This method ensures that all cells remain balanced throughout the charging process. Alternatively, using a 24V LiFePO4 battery charger or a 48V LiFePO4 battery charger designed for the entire system voltage can simplify the charging process while maintaining balance among the batteries.
Safe Charging Guidelines for LiFePO4 Batteries
- Inspect for Damage:
Before charging, inspect the battery for any physical damage such as dents, leaks, or swelling. Charging a damaged battery can lead to safety hazards and should be avoided.
- Use Recommended Chargers:
Always use chargers specifically designed for LiFePO4 batteries. These chargers are equipped with the necessary voltage and current settings suitable for safe charging without overcharging or overheating the battery.
- Avoid Overcharging:
LiFePO4 batteries are sensitive to overcharging, which can lead to reduced lifespan and potential safety hazards. Use chargers that automatically stop charging once the battery reaches full capacity or employ chargers with built-in protection circuits.
- Monitor Charging Temperature:
LiFePO4 batteries should be charged within a specific temperature range (typically between 0°C to 45°C or as specified by the manufacturer). Charging at temperatures outside this range can damage the battery or compromise safety.
- Charge at Moderate Rates:
Charging LiFePO4 batteries at moderate rates (typically 0.5C to 1C) is recommended for optimal performance and safety. Charging at excessively high rates can generate heat and stress the battery, leading to reduced longevity.
- Avoid Deep Discharge:
While LiFePO4 batteries are less susceptible to damage from deep discharge cycles compared to other lithium-ion chemistries, it is still advisable to avoid deep discharge whenever possible. Regularly deep discharging the battery can shorten its lifespan.
- Store Batteries Safely:
When not in use, store LiFePO4 batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Proper storage helps maintain battery performance and prolongs lifespan.
Safety Instruction During Charging LiFePO4 Battery
Charge in a Well-Ventilated Area: Charging any type of battery can generate heat and gases. Ensure adequate ventilation to dissipate heat and prevent the accumulation of potentially hazardous gases.
Avoid Charging Unattended: While modern chargers have safety features, it is advisable to supervise the charging process whenever possible, especially when using older or less advanced chargers.
Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Always refer to the manufacturer's recommendations and guidelines for charging LiFePO4 batteries. Each battery model may have specific requirements that should be followed to ensure safe and effective charging.
How to Charge LiFePO4 Batteries with Solar?
Charging LiFePO4 batteries with solar power is an excellent option for off-grid applications and renewable energy systems. To charge LiFePO4 batteries using solar power, you should:
- Select a Solar Panel: Choose one with suitable voltage and wattage ratings for LiFePO4 batteries.
- Install a Charge Controller: Use a controller designed for LiFePO4 batteries to regulate charging and protect against overcharging.
- Connect and Monitor: Wire the solar panel to the charge controller, then connect the controller to the battery. Monitor charging to ensure it stays within safe limits.
- Optimize and Secure: Adjust panel orientation for maximum sunlight exposure and secure all components against weather and theft.
FAQs on Charging LiFePO4 Battery
Q: How much power is left in LiFePO4 batteries for best charging?
A: LiFePO4 batteries are best charged when the remaining power is 25%-30%, so as to ensure that the battery will not be over-discharged. In addition, if the electric vehicle is not used for a long time, it should be charged once every 3 months, and each charge should be 100% full.
Q: How often should I charge my LiFePO4 battery?
A: LiFePO4 batteries can be charged whenever convenient, as they do not suffer from memory effect. However, avoid deep discharges to prolong battery life.
Q: Can I charge LiFePO4 batteries with other batteries charger?
A: It is not recommended to charge LiFePO4 battery with a normal charger, whatever a lead acid charger or lithium-ion battery charger. LiFePO4 batteries have specific voltage and current requirements that differ from other lithium-ion chemistries.
Q: What should I do if my LiFePO4 battery becomes hot during charging?
A: Immediately disconnect the charger and allow the battery to cool down in a safe place. Check for any abnormalities before attempting to charge again.
Q: How many amps should I charge a LiFePO4 battery?
A: Typically, LiFePO4 batteries can be charged at a rate of 0.2C to 0.5C, where C is the capacity of the battery in ampere-hours (Ah). For example, a 10Ah LiFePO4 battery can be charged at a standard rate of 5A (0.2C) to 10A (0.5C). Always refer to the battery manufacturer's specifications for the recommended charging current.
Conclusion
Charging LiFePO4 batteries safely is essential to maximize their performance, lifespan, and safety. By following the recommended charging guidelines, using appropriate charger for LiFePO4, and monitoring the charging process, you can ensure that your LiFePO4 batteries operate efficiently and safely throughout their lifespan.

Redodo

Redodo
Recent Post

How Long Does a Trolling Motor Battery Last?

Convert RV from Lead-Acid to Lithium Battery: A Complete Guide

How Long Will a 200Ah Battery Run an Air Conditioner?

A Full Review of Redodo 12V 140Ah Group 31 Deep Cycle Battery




![⚡[$294 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 140Ah Group 31 Lithium Battery with Bluetooth | 40% More Capacity | For RV, Marine, Solar Home](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo_12V_140ah_bluetooth_battery_ee6d5fd1-5c7d-4b9a-90ab-d54d06b29a04.jpg?v=1742967763)
![⚡[$377 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 200Ah Lithium LiFePO4 Battery | 1280W Load Power | For RV, Solar, Off-Grid](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo12V200ahlithiumbattery.jpg?v=1735892910)
![⚡[$239 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 100Ah Group 24 Bluetooth LiFePO4 Battery | Real-Time Battery Monitoring | For RV, Marine, Solar](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo_12V_100Ah_group_24_bluetooth_lithium_battery.jpg?v=1744253032)
![⚡[$220 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 100Ah Lithium Trolling Motor Battery With Low Temp Protection](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo12V100Ahlow-tempbattery.webp?v=1738462317)
![⚡[$220 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 100Ah Group 24 Deep Cycle LiFePO4 Lithium Battery | For Home, RV, Marine](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo_12V_100Ah_group_24_lithium_battery_6301965d-f6e8-467f-825f-3eec839b3e1f.jpg?v=1744105344)
![⚡[$220 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery | Best Budget | For RV, Solar, Trolling Motor](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo_12v_100ah_lithium_battery_b9015ddd-64b5-4be2-8c88-392f0bb4ab30.jpg?v=1742973160)