Lithium-ion batteries are essential in powering modern electronics, from smartphones to electric vehicles. A common concern is how long these batteries can last without charging. This article focuses on the factors influencing the lifespan of lithium-ion batteries, and tips for long-term storage battery and prolonging these batteries life.
Table of Content
- What is a Lithium-ion Battery?
- How Do Lithium-ion Batteries Work?
- How Long Do Lithium-Ion Batteries Last?
- Storage Conditions for Lithium-ion Batteries
- Tips for Prolonging Lithium Battery Lifespan
- How Do I Know How Much Charge is Left in My LiFePO4 Lithium Battery?
- FAQs on Lithium-ion Battery
What is a Lithium-ion Battery?
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are rechargeable power sources that rely on lithium ions to store and release energy. They are known for their high energy density, lightweight, and long cycle life, making them ideal for various portable electronics and electric vehicles.
Different from lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries are known for their high energy density, lightweight, and longer lifespan, making them ideal for modern portable electronics and electric vehicles. These differences make lithium-ion batteries more suitable for high-performance, lightweight applications.
How Do Lithium-ion Batteries Work?
Li-ion batteries consist of a positive electrode (cathode), a negative electrode (anode), and an electrolyte that facilitates the movement of lithium ions between the electrodes. During discharge, lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode, generating an electric current. When charging, the ions travel back to the anode.

(Image: Let's talk Science)
How Long Do Lithium-Ion Batteries Last?
There are several different types of lithium batteries, including ternary lithium batteries and lithium manganese oxide batteries. These lithium batteries are known for their higher energy density, which allows them to store more energy in a smaller volume. However, these lithium batteries can only last 300 to 500 cycles, typically around 2-3 years.
On the other hand, lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) battery, a new type of lithium battery, offers a longer lifespan, even though their energy density is lower compared to other lithium battery types.
For instance, Redodo LiFePO4 battery boast a cycle life of over 4,000 cycles, that means it can translate to more than 10 years of regular use. This makes them an excellent alternative to traditional lead-acid batteries, combining the benefits of extended life and improved safety.
While without charging, a well-maintained lithium-ion battery can last between 2 to 6 months before it loses a significant amount of its capacity. Specific durations can vary depending on the battery's age, chemistry, and storage conditions.
Even when not in use, lithium-ion batteries gradually lose their charge due to self-discharge. The self-discharge rate for lithium-ion batteries is relatively low, typically around 2-3% per month when stored at room temperature. However, this rate can increase with higher storage temperatures.
Storage Conditions for Lithium-ion Batteries
Proper storage conditions are crucial for minimizing self-discharge and maintaining battery health, including temperature, state of charge, humidity, and ventilation.
1. Temperature
Temperature plays a significant role in the performance and lifespan of lithium-ion batteries. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can negatively affect battery health.
- Ideal Storage Temperature: The optimal storage temperature for lithium-ion batteries is around 20°C (68°F). Keeping batteries in a cool environment helps reduce the rate of self-discharge and prevents thermal degradation.
- Avoid High Temperatures: High temperatures can accelerate the self-discharge rate and cause internal components to degrade faster. This can lead to reduced capacity and a shorter overall lifespan. Avoid storing batteries in direct sunlight or near heat sources.
- Avoid Freezing Temperatures: Extremely low temperatures can also damage lithium-ion batteries. While cold storage can reduce the self-discharge rate, temperatures below 0°C (32°F) can cause the electrolyte to become unstable and lead to permanent damage.

2. State of Charge (SoC)
The state of charge at which you store lithium-ion batteries significantly impacts their health and longevity.
- Optimal SoC for Storage: It's recommended to store lithium-ion batteries at a charge level of around 40-60%. Storing them fully charged (100%) or fully discharged (0%) can accelerate capacity loss over time.
- Periodic Recharging: For long-term storage, periodically check the battery's charge level and recharge it to the optimal storage level if it drops too low. This helps prevent deep discharge, which can lead to irreversible damage.

3. Humidity
Excessive humidity can lead to internal corrosion and other issues that affect battery performance.
- Dry Environment: Store lithium-ion batteries in a dry environment to prevent moisture from entering the battery casing. Using silica gel packs or other moisture-absorbing materials can help maintain a low-humidity environment.
- Avoid Water Exposure: Ensure that the storage area is free from water exposure and leaks, as even a small amount of water can cause significant damage to the battery.
4. Ventilation
Proper ventilation is important to prevent the buildup of heat and gases.
- Ventilated Area: Store batteries in a well-ventilated area to allow any heat generated to dissipate. This is particularly important if you are storing multiple batteries together.
- Avoid Enclosed Spaces: Do not store batteries in tightly enclosed spaces where heat can accumulate, as this increases the risk of thermal runaway.
In short, it's advisable to periodically check and recharge the batteries to around 50% to maintain its health, and put them in a dry, ventilated and suitable temperature environment. Checking every 3-6 months and recharging as necessary can help prevent deep discharge, which can permanently damage the battery.
Read More: A Comprehensive Guide on How to Store LiFePO4 Batteries
Tips for Prolonging Lithium Battery Lifespan
1.Avoid extreme temperatures: Keep batteries away from high heat or freezing temperatures.
2.Moderate charge levels: Avoid keeping batteries fully charged or fully discharged for extended periods.
3.Periodic charging: Even when not in use, charge the battery to around 50% every few months.
4.Avoid deep discharge: Try not to let the battery discharge completely before recharging.
5.Avoid fast charging and discharging: Rapid charging or discharging can generate excess heat, which may cause damage to the battery's internal components over time, reducing its overall lifespan.
6.Use original equipment manufacturer (OEM) chargers: Using OEM chargers designed specifically for Li-ion batteries ensures that they receive the correct voltage and current, preventing damage and prolonging their lifespan. Redodo provides suitable LiFePO4 battery chargers for charging LiFePO4 lithium batteries.
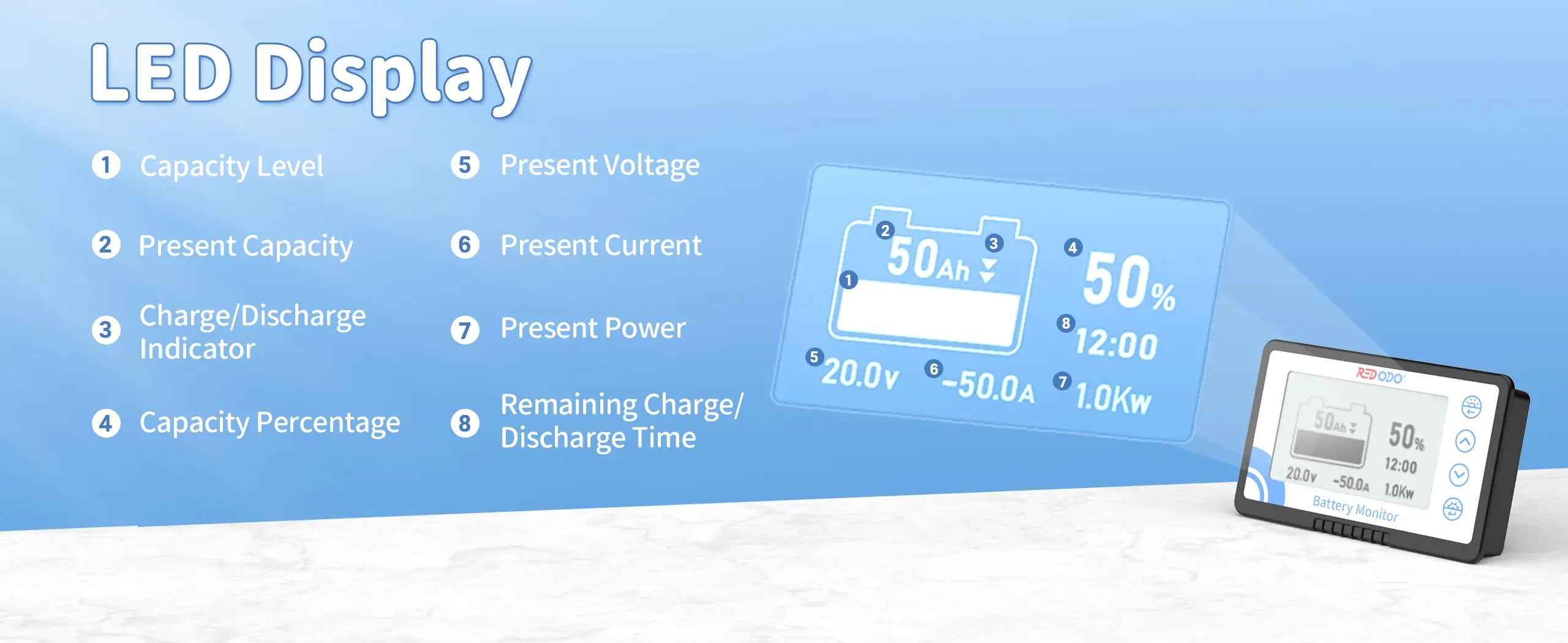
How Do I Know How Much Charge is Left in My LiFePO4 Lithium Battery?
Many LiFePO4 batteries have built-in battery management systems that display the remaining charge as a percentage on a digital screen or through a battery gauge. If your battery system includes a battery monitoring system (BMS), you can check the charge status via a connected app or interface, which often provides detailed information about voltage, current, and state of charge.
For those using standalone LiFePO4 batteries in applications like solar energy storage or electric vehicles, a battery monitor can be used to measure the battery’s charge level. Recommend to use Redodo Battery Monitor to know your battery's remaining capacity, which is compatible with various types of battery like lithium Iron Phosphate, lithium-ion, LifePO4, and lead acid batteries.
Regularly checking these indicators helps you maintain the battery’s health and ensures efficient usage.
FAQs on Lithium-ion Battery
1. Why LiFePO4 Lithium-ion Battery Can Last Longer?
The longevity of LiFePO4 batteries, lasting between 5 to 10 years, is primarily due to their stable chemical composition, high cycle life, thermal stability, built-in safety features, minimal self-discharge, consistent performance, and environmentally friendly materials. These attributes make LiFePO4 batteries an excellent choice for various applications, where long-term reliability and efficiency are paramount.
2. Is LiFePO4 Battery Safer Than Lithium-ion Battery?
Yes, LiFePO4 battery is considered safer than traditional Lithium-Ion batteries. This is because LiFePO4 batteries have a more stable chemistry compared to Li-ion batteries and are less prone to overheating, thermal runaway, and other safety issues. LiFePO4 batteries also have a lower risk of thermal runaway due to their lower internal resistance, which means they generate less heat and reduce the likelihood of cell damage or explosion.
3. Is It Safe to Store Lithium-ion Batteries for a Long Time?
Yes, it is safe to store lithium-ion batteries for long periods if they are kept in a cool, dry place and at a charge level of around 40-60%.
4. Can I Use Any Charger for My Lithium-ion Battery?
It's recommended to use chargers specifically designed for your battery type to prevent overcharging and overheating, which can damage the battery.
Learn more: Can I Charge LiFePO4 Battery with a Normal Charger?
5. Do Lithium Batteries Need to Be Stored Fully Charged?
No. Storing a lithium-ion battery fully charged can accelerate its degradation. To prolong your battery’s life, it's better to store it at around 40-60% charge.
6. How Can I Tell If My Battery Needs to Be Replaced?
Signs that a battery needs replacement include a significantly reduced runtime, the battery not holding a charge, or the device shutting down unexpectedly.
Conclusion
Lithium-ion batteries offer a long lifespan, both in terms of charge cycles and overall years of use, thanks to their advanced chemistry and efficient design. Even when not in use, they can retain their charge for several months if stored correctly. Proper care, such as avoiding extreme temperatures and maintaining an optimal charge level during storage, can further extend their lifespan, ensuring they remain reliable power sources for various applications.
For more insights into lithium-ion battery, explore our other blogs or contact us at our website Redodopower.com. Don't miss out on subscribing to our newsletters for valuable information about lithium battery, exclusive promotions, and more!

Redodo

Redodo
Recent Post

How Long Does a Trolling Motor Battery Last?

Convert RV from Lead-Acid to Lithium Battery: A Complete Guide

How Long Will a 200Ah Battery Run an Air Conditioner?

A Full Review of Redodo 12V 140Ah Group 31 Deep Cycle Battery



![⚡[$220 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery | Best Budget | For RV, Solar, Trolling Motor](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo_12v_100ah_lithium_battery_b9015ddd-64b5-4be2-8c88-392f0bb4ab30.jpg?v=1742973160)
![⚡[$220 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 100Ah Group 24 Deep Cycle LiFePO4 Lithium Battery | For Home, RV, Marine](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo_12V_100Ah_group_24_lithium_battery_6301965d-f6e8-467f-825f-3eec839b3e1f.jpg?v=1744105344)
![⚡[$220 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 100Ah Lithium Trolling Motor Battery With Low Temp Protection](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo12V100Ahlow-tempbattery.webp?v=1738462317)
![⚡[$239 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 100Ah Group 24 Bluetooth LiFePO4 Battery | Real-Time Battery Monitoring | For RV, Marine, Solar](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo_12V_100Ah_group_24_bluetooth_lithium_battery.jpg?v=1744253032)
![⚡[$220 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 100Ah Group 31 Bluetooth Lithium Battery | Real-Time Battery Monitoring | For RV, Marine, Solar](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo12V100Alithiumbatterywithbluetoothconnection.webp?v=1744698930)
![⚡[$220 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 100Ah Mini Lithium LiFePO4 Battery | Smallest Battery | For RV, Trolling Motor, Solar](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo12V100AhMiniLiFePO4LithiumBattery.jpg?v=1739959054)

![⚡[$294 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 140Ah Group 31 Lithium Battery with Bluetooth | 40% More Capacity | For RV, Marine, Solar Home](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo_12V_140ah_bluetooth_battery_ee6d5fd1-5c7d-4b9a-90ab-d54d06b29a04.jpg?v=1742967763)