Are you struggling with a lithium-ion battery that won't charge? Before you panic and rush to the store for a replacement, there are a few potential solutions you can try to revive your battery. In this article, we will guide you through the process of fixing a lithium-ion battery that won't charge.
Table of Content
- How Do Lithium Batteries Charge?
- Why Is RV/Marine Lithium Battery Not Charging?
- Troubleshooting Tips to Fix RV/Marine Lithium Battery Problems
- Can a Dead Lithium Battery Be Recharged?
How Do Lithium Batteries Charge?
Before studying the lithium battery problems, let's first understand how lithium batteries are charged.
Lithium-ion batteries charge through the process of lithium ions moving between two electrodes - the anode (positive electrode) and cathode (negative electrode) - within an electrolyte solution. When the battery is connected to a charger, an electrical current flows into the battery, causing lithium ions to move from the positive electrode to the negative electrode.
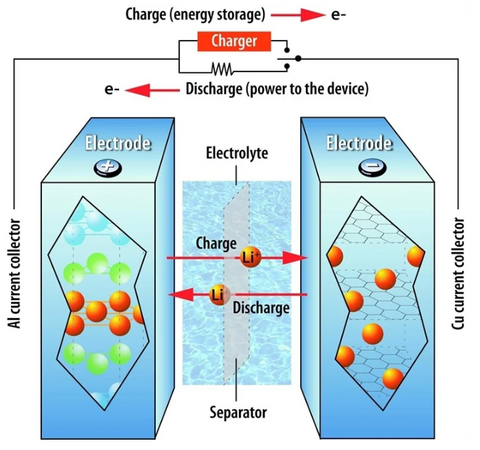
This process is known as the charging or recharging cycle. During discharge, the process is reversed, with lithium ions moving from the negative electrode to the positive electrode, generating electricity to power the device. This cycle of charge and discharge can be repeated multiple times.
Why Is RV/Marine Lithium Battery Not Charging?
Battery Protection Mechanisms Engaged
Lithium batteries used in RVs and marine applications not charging due to several reasons. One common reason is when the battery's protection mechanisms engage.
Lithium batteries have built-in protection circuits that monitor and regulate voltage, temperature, and current. If any of these parameters go beyond safe limits, the battery protection circuit will shut off the battery to prevent damage. This may occur if the battery is exposed to extreme temperatures, overcharged, or discharged too quickly. It is crucial to ensure proper charging and discharging practices to avoid triggering these protection mechanisms.

1. Deep Discharge
Deep discharging, where the battery is discharged to extremely low levels, can also contribute to premature failure of lithium batteries in RVs and marine applications. Lithium batteries are not designed to be fully drained, and deep discharges can strain the battery, leading to irreversible damage. It is advisable to monitor the battery voltage and avoid discharging it below recommended levels.
2. Overcharging
Overcharging is another common reason for lithium battery failure. If the battery is continuously charged beyond its intended voltage or for extended periods, it can lead to overheating, which can damage the battery cells. It is essential to use a proper charger specifically designed for lithium batteries and avoid overcharging them.
3. Over current
Overcurrent can also be a factor that can lead to the premature death of lithium batteries. Overcurrent occurs when the battery is subjected to a higher current than it is designed to handle. This can happen due to a faulty charging system or by using a charger that is not compatible with the battery.
When a lithium battery is subjected to overcurrent, it can cause overheating and thermal runaway, which can be extremely dangerous. Overcurrent can damage the battery's internal structure and lead to a decrease in its overall capacity and performance. In severe cases, it can even lead to the battery swelling, leaking, or catching fire.
To prevent overcurrent, it is important to use a charger that is specifically designed for lithium batteries and follow the manufacturer's recommended charging specifications. Additionally, regularly inspecting the battery and charging system for any signs of damage or wear can help identify potential issues before they become severe.
4. Short circuit
A short circuit occurs when there is an unintended connection or low resistance path between the positive and negative terminals of the battery. This can lead to a significant increase in current flow, causing excessive heat generation and potentially damaging the battery.
Short circuits can occur due to various reasons, such as damaged or frayed wiring, improper installation, or accidental contact with conductive materials. When a short circuit happens, it can result in irreversible damage to the battery, including internal heat buildup, electrolyte leakage, or even a thermal runaway event, which can be dangerous and lead to a battery fire or explosion.
To prevent short circuits, it is essential to handle and install lithium-ion batteries carefully, ensuring proper insulation and protection of the terminals. Avoid exposing the battery to conductive materials, such as metal objects or liquids that can cause a short circuit. Regularly inspect and maintain the wiring and connections to identify any potential issues early on and address them promptly.
Choose Redodo Smart Bluetooth LiFePO4 battery with upgraded BMS(battery management system), which provides short circuit protection, overcharge protection and more for each battery.
5. High/Low Temperature
Exposing lithium batteries to high temperatures can accelerate their degradation and lead to a loss of capacity. High temperatures can cause the electrolyte inside the battery to break down faster, leading to a decrease in performance and lifespan. Additionally, high temperatures can increase the risk of thermal runaway, which can result in swelling, leakage, or even fire. It is crucial to avoid exposing lithium batteries to excessive heat, whether during usage, charging, or storage.
On the other hand, subjecting lithium batteries to extremely low temperatures can also have negative effects. In freezing temperatures, the battery's electrolyte can suffer from reduced mobility, inhibiting the movement of lithium ions and resulting in decreased performance.
Cold temperatures can also cause the battery's internal resistance to increase, leading to voltage drops and reduced capacity. Therefore, some batteries like Redodo 12V 100Ah low temperature protection batteries have the low temperature protection. When its under freezing point, it will cut off the charging automatically.
Insufficient Voltage Output
One possible reason for lithium battery charging issues is the use of a charger with insufficient voltage output. Chargers are responsible for supplying the necessary voltage to recharge the battery. If the charger's output voltage is too low, the battery will not charge properly. To avoid this issue, it is crucial to use a charger that matches the correct voltage output for your specific lithium battery. To determine the appropriate voltage specifications for different LiFePO4 battery packs and systems, refer to the table provided below.

Can I charge LiFePO4 battery with a normal charger? Well, to be honest, not recommended. LiFePO4 batteries have different charging requirements and use a different charging logic compared to lead-acid batteries. Charging a LiFePO4 battery with a lead-acid charger may not fully charge the LiFePO4 battery and could potentially damage it over the long term. It is important to use a LiFePO4 battery charger specifically designed for charging LiFePO4 lithium batteries to ensure proper charging and prolong the lifespan of the battery.
Battery Age
Like all batteries, lithium batteries have a limited lifespan. Over time, they naturally degrade and lose their capacity to hold a charge, eventually leading to failure.
Manufacturing Defects
In some cases, lithium batteries may have manufacturing defects that cause them to fail earlier than expected. This is why it is important to purchase batteries from reputable manufacturers like Redodo which has the UL, FCC, CE, ROSH, UN38.3 certification.
Troubleshooting Tips to Fix RV/Marine Lithium Battery Problems
Verify Your Connections Once More
If you find that your lithium battery isn't charging properly, it's crucial to carefully examine all of your connections. Take the time to wiggle the wires and inspect for any loose connections that might require tightening. This includes the battery connections as well as any other connections within your electrical system. Even a slightly loose connection could lead to complications, including difficulties in charging your batteries. By tightening any loose connections and retesting your system, you may discover that this resolves the problem.
Use a Clamp-On Ammeter and Volt Meter
To safely test the flow of electricity in your system, consider using a clamp-on ammeter and volt meter. These tools allow you to easily measure the amps and volts without the need to disconnect any wires. This is important for identifying any potential issues in your system.
By measuring the amps flowing in and out of your batteries, you can determine if each battery is contributing equally when drawing power. If one battery is being overworked, it can shorten its lifespan and prevent your lithium battery from charging properly.
You can also use the meter to test the voltages at both the batteries and the charger. A voltage higher than the battery's nominal 13.2 volts indicates that it is being charged. If the voltage is too low, it may indicate a problem with your charger.
Ensure You Have an Appropriate Charger
To ensure the proper charging of your lithium battery, it is important to have a suitable battery charger. If you have recently installed a lithium battery into your existing electrical system, your current charger may not be adequate.
Unlike other battery types, lithium batteries can handle higher levels of power and require faster charging. As a result, you may need to upgrade your charger or adjust its settings to match the requirements of your lithium batteries. It is recommended to consult the documentation provided with your charger and batteries to ensure compatibility and appropriate charging.
Store and handle batteries properly
To ensure the safety and longevity of lithium batteries, it is important to follow proper storage guidelines. These include keeping them away from heat sources like radiators, as high temperatures can cause them to overheat and potentially explode.
Additionally, it is crucial to store lithium batteries away from conductive objects that may accidentally cause a short circuit. If a battery exhibits any abnormal behavior such as strange odors, liquid leakage, physical deformation, or other anomalies after removal, it should not be used.
Lastly, it is advised to avoid keeping LiFePO4 batteries in strong magnetic fields during storage, as these fields can disrupt or damage the battery management system. Following these storage precautions will help maintain the safety and functionality of lithium batteries.
Seek Professional Assistance
If you have followed all troubleshooting steps and are still unable to fix the charging problem, it is recommended to seek professional assistance. You can reach out to the manufacturer or a qualified technician who can analyze the issue and provide expert guidance or repair services.
Can a Dead Lithium Battery Be Recharged?
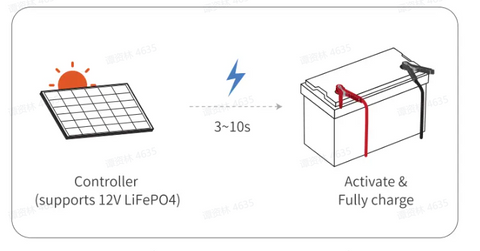
When a battery is discharged to the point of being completely depleted, it can be classified as a dead battery. If a lithium battery is left unused for an extended period of time, it may enter a dormant state due to self-discharge, resulting in a loss of power. Here are 2 functions to recover the dead lithium battery.
1. Use a charger with a 0V charging function to fully charge the battery.

2. Connect a solar charge controller that supports your LiFePO4 battery voltage charging to charge the battery for 3~10s in sunny daytime.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed common reasons that causes lithium batteries not charging and some troubleshooting tips. The LiFePO4 lithium batteries from Redodo have 5 years warranty. If you have any problems with the battery, can email service@redodopower.com to seek for help and we will be always here for you!


Redodo

Redodo
Recent Post

How Long Will a 200Ah Battery Run an Air Conditioner?

A Full Review of Redodo 12V 140Ah Group 31 Deep Cycle Battery

How Much Does it Cost to Replace Golf Cart Batteries?

What Size Fish Finder Battery Do I Need? 2025 Updated







![⚡[$165 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery | Best Budget | For RV, Solar, Trolling Motor](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo_12v_100ah_lithium_battery_b9015ddd-64b5-4be2-8c88-392f0bb4ab30.jpg?v=1742973160)
![⚡[$161 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 100Ah Group 24 Deep Cycle LiFePO4 Lithium Battery | 20% Smaller | For Home, RV, Marine](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/group_24_3255e3e9-409d-412d-8871-4f05861a5c1e.jpg?v=1742968223)
![⚡[$165 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 100Ah Lithium Trolling Motor Battery With Low Temp Protection](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo12V100Ahlow-tempbattery.webp?v=1738462317)
![⚡[$184 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 100Ah Group 31 Bluetooth Lithium Battery | Real-Time Battery Monitoring | For RV, Marine, Solar](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/GROUP_31_0501cb0c-ed50-4c4a-b78e-b7ab501d90b4.jpg?v=1742971970)
![⚡[$198 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 100Ah Mini Lithium LiFePO4 Battery | Smallest Battery | For RV, Trolling Motor, Solar](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo12V100AhMiniLiFePO4LithiumBattery.jpg?v=1739959054)
![⚡[$238 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 140Ah Group 31 Lithium Battery with Bluetooth | 40% More Capacity | For RV, Marine, Solar Home](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo_12V_140ah_bluetooth_battery_ee6d5fd1-5c7d-4b9a-90ab-d54d06b29a04.jpg?v=1742967763)
![⚡[$340 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 200Ah Lithium LiFePO4 Battery | 1280W Load Power | For RV, Solar, Off-Grid](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo12V200ahlithiumbattery.jpg?v=1735892910)
![⚡[$496 after Sign-Up] Redodo 12V 300Ah Lithium LiFePO4 Battery | Replaces 6*12V 100Ah AGM Batteries | RV, Marine, Solar](http://www.redodopower.com/cdn/shop/files/Redodo_12V_300Ah_Lithium_Battery_fe27f603-e18b-4c4a-9105-848685f2fcdb.jpg?v=1743157570)